Understanding the Basics of Internet Speed
Internet speed is a crucial factor that influences our ability to engage in various online activities, such as streaming, gaming, browsing, and downloading. At its core, internet speed refers to how quickly data is transmitted over a connection, impacting how efficiently users can interact with online content. Two fundamental concepts that govern internet speed are bandwidth and latency.
Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted in a given time, typically measured in megabits per second (Mbps). Higher bandwidth allows multiple users to access the internet simultaneously without significant slowdowns, making it essential for households with multiple devices. On the other hand, latency refers to the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the destination and back again. Measured in milliseconds (ms), lower latency is preferred for activities that require real-time interaction, such as online gaming or video conferencing.
Different types of internet connections deliver various speeds and performance levels. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) uses existing telephone lines to provide internet access, generally offering moderate speeds suitable for everyday browsing and streaming. Cable internet utilizes coaxial cables and tends to provide faster speeds than DSL, making it ideal for larger households with high bandwidth demands. In contrast, fiber optic internet harnesses light to transmit data via thin glass or plastic fibers, offering the highest speeds and reliability, particularly beneficial for activities that require robust connectivity.
Several factors can impact your internet speed, including network congestion during peak usage times, the distance from the router, and the type of device being used. Additionally, age or limitations of the physical infrastructure can hinder performance. Understanding these elements helps users troubleshoot issues effectively and make informed decisions when it comes to technology upgrades or provider changes.
Identifying the Causes of Slow Internet
Experiencing slow internet can be frustrating, and understanding the potential causes is an essential step toward regaining optimal connectivity. One of the most prevalent reasons for reduced internet speed is network congestion. This occurs when multiple devices are simultaneously using the same network resources, which can lead to reduced bandwidth for each device. Factors such as peak usage times, where numerous users are online, can exacerbate this issue.
Another common cause of slow internet is outdated hardware. Routers and modems are critical components in your internet setup, and older models may not support higher speeds offered by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Regularly checking for firmware updates and considering an upgrade to newer technology can significantly improve speed and reliability.
Interference from other devices also plays a vital role in internet performance. Wireless signals can be disrupted by electronic devices such as microwaves, cordless phones, and even neighboring Wi-Fi networks. It is advisable to position your router away from such devices and to select the least congested Wi-Fi channel available in the settings of your router.
Additionally, software problems can contribute to slow internet speeds. Malware or resource-heavy applications running in the background can consume bandwidth and processor power. Performing regular maintenance, including virus scans and managing startup programs, can help mitigate these issues.
For users facing sluggish internet, conducting simple troubleshooting steps is advisable. Restarting the router, checking for interference, and updating firmware can often resolve connectivity issues. Understanding these common causes will assist in systematically addressing and improving your internet speed, ensuring a smoother online experience.
Checking Your Internet Speed
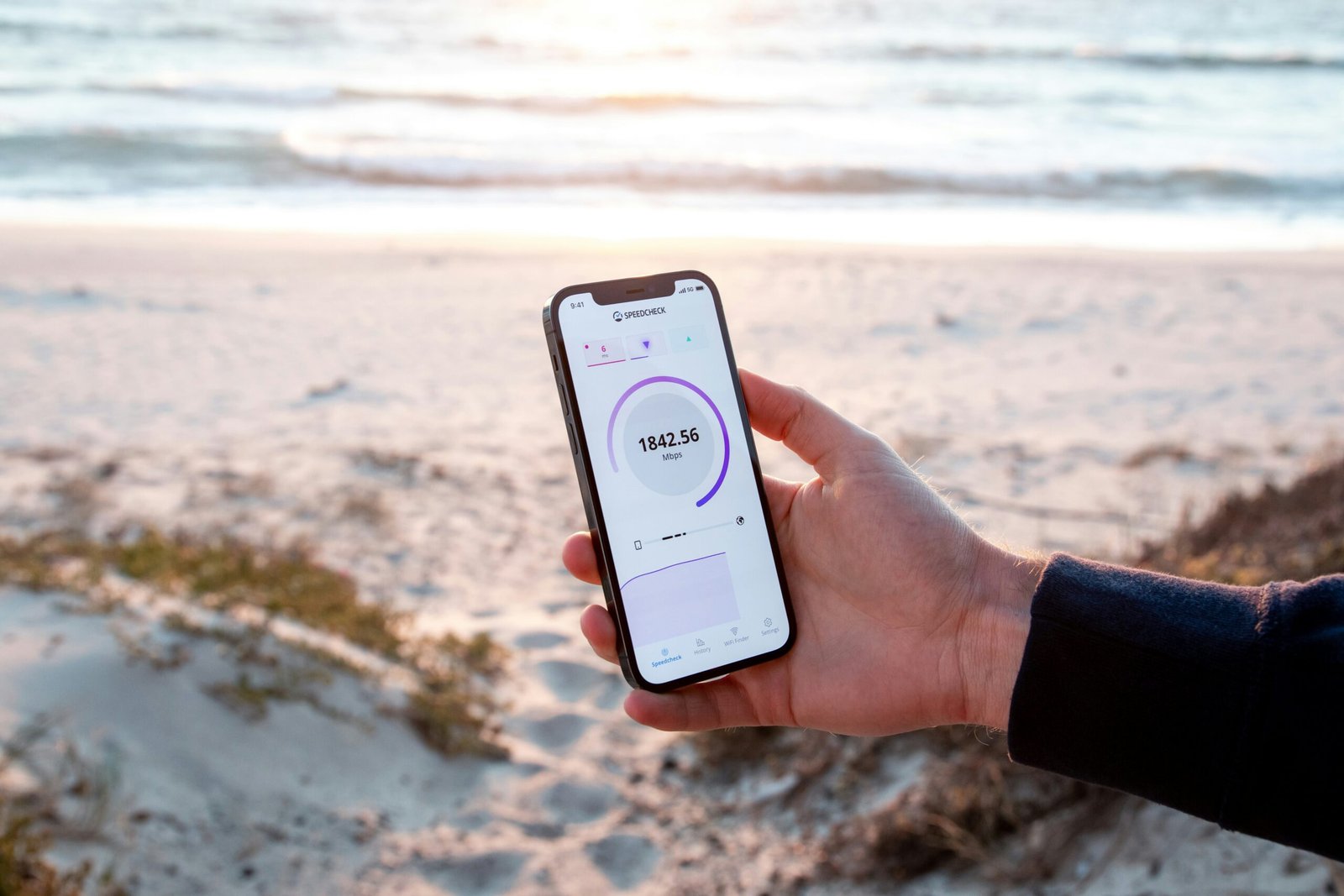
Monitoring your internet speed is a crucial step in determining the quality of your connection, especially if you are experiencing slow performance. Using speed test tools can provide a clear and reliable assessment of your internet speed, helping identify potential issues. Numerous speed testing websites and applications are available for this purpose, including renowned options such as Ookla’s Speedtest, Fast.com, and Google’s speed test feature. These tools are user-friendly and can be accessed on various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and computers.
To initiate a speed test, simply visit your chosen speed testing website or open the application, then click on the “Go” or “Start” button. The tool will measure different aspects of your connection, including download speed, upload speed, and ping (latency). Download speed indicates how quickly data can be transferred to your device, while upload speed reflects how swiftly data can be sent from your device to the internet. Ping measures the delay before a transfer of data begins, with lower values indicating a more responsive connection.
After the test is complete, the results will display the measured speeds in megabits per second (Mbps). To understand whether your current speeds align with the promises made by your Internet Service Provider (ISP), compare the results to the speed tier you subscribed to. Keep in mind that fluctuations in speed may occur due to various factors such as network congestion during peak usage times or limitations of the hardware being used.
If the results indicate that your speeds are consistently below what your ISP promised, it may be worth investigating further to pinpoint the causes of the slow internet connection. Regularly checking your internet speed can help you stay informed about your service quality and assist in addressing any issues that arise.
Optimizing Your Wi-Fi Connection
Enhancing your Wi-Fi connection is crucial for ensuring a stable and fast internet experience. Several techniques can significantly improve the performance of your Wi-Fi network, beginning with the strategic placement of your router. Ideally, your router should be positioned in a central location within your home or office to minimize signal obstructions caused by walls, furniture, or appliances. The higher the router is placed, the better the coverage, as signals can propagate more effectively. Avoid placing it near metallic objects or electronic devices that might create interference.
Another key strategy is to change your Wi-Fi channel. Many routers operate on the same few channels, particularly in densely populated areas. Utilizing a less congested channel can improve your connection speed and stability. Most routers allow you to scan for less crowded channels through their settings interface. Regularly surveying your network environment to adjust channels as necessary can lead to noticeable enhancements in performance.
Interference from other devices, such as microwaves and cordless phones, can also degrade your Wi-Fi signal. To minimize this interference, try to keep these devices away from your router. Additionally, securing your network with a strong password will prevent unauthorized access that can consume bandwidth, inevitably slowing down your internet speed.
Keeping your router’s firmware updated is essential for optimal performance and security. Manufacturers often release updates that enhance functionality and address vulnerabilities. Frequent checks for available firmware updates through your router’s administration panel can ensure that you are using the latest technology available.
If you find that your Wi-Fi connection still struggles despite these efforts, consider using Wi-Fi extenders to amplify the signal in areas of your home that experience weak connectivity. By employing these various techniques, you can significantly enhance the performance of your Wi-Fi connection, ultimately leading to a fast and reliable internet experience.
Upgrading Your Hardware
One of the primary factors influencing internet speed is the hardware utilized in your network, specifically your router and modem. Outdated equipment can significantly hinder performance, leading to slower speeds and unreliable connections. As technology advances, newer standards and protocols are developed to provide enhanced speeds and greater efficiency. Therefore, upgrading your hardware can often result in substantial improvements to your overall internet experience.
When evaluating your current router and modem, it’s essential to consider the internet speeds offered by your service provider. If your existing devices cannot support these speeds, you may find yourself at a disadvantage. For example, if you subscribe to a plan that offers 200 Mbps but your modem only supports 100 Mbps, you will not be able to capitalize on the full potential of your internet package. To ensure you are choosing the right hardware, look for a modem and router combination that supports at least the highest speed available from your ISP.
Furthermore, different connection types—such as DSL, cable, and fiber—require specific types of routers and modems. For instance, cable modems use a different technology compared to DSL modems, making it crucial to select the appropriate hardware that aligns with your internet service type. In addition, newer models often come equipped with dual-band or tri-band technology, allowing for better distribution of bandwidth across multiple devices.
Ultimately, investing in a modern router or modem can significantly enhance your network’s performance. This upgrade not only ensures compatibility with higher-speed internet plans but also offers advanced features such as improved security protocols and extended Wi-Fi coverage, enabling a more stable and faster internet connection throughout your home.
Limiting Bandwidth Usage
To enhance overall internet performance, it is essential to manage bandwidth consumption within your household. One of the most effective strategies is to identify and limit the number of connected devices. Every device connected to your network consumes a portion of available bandwidth, so periodically reviewing and disconnecting unused devices can lead to noticeable improvements in speed.
Prioritizing essential devices is another critical step in managing bandwidth usage. For example, if multiple users are streaming videos or playing online games, this can significantly strain your internet connection. To address this, you can set up Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router. QoS enables you to give priority to specific devices or applications, ensuring that, for instance, a gaming console or video conferencing application receives the necessary bandwidth for optimal performance, even when other devices are active.
Furthermore, optimizing the settings in applications that consume substantial bandwidth can markedly improve your internet speed. Many modern streaming platforms allow users to adjust their video quality settings. Lowering the resolution helps conserve bandwidth while still providing a satisfactory viewing experience. Similarly, online gaming platforms often feature options that reduce graphic quality or limit data usage, ensuring smoother gameplay without excessive interruptions.
Moreover, it is important to regularly check for software updates on your devices and applications, as these upgrades often come with performance optimizations that can enhance efficiency. By combining device management, prioritization of essential functions, and application optimization, you can successfully limit bandwidth usage in your household, thereby achieving a more stable and faster internet connection.
Troubleshooting Software Issues
When experiencing a decrease in internet speed, one of the first areas to examine is the software running on your device. Various software-related issues can significantly affect your internet performance, including malware infections, background applications consuming bandwidth, and configuration errors. Identifying and addressing these issues is critical in restoring optimal internet speed.
Malware is a pervasive cause of reduced internet speeds. Malware can hijack your network connection, leading to slowdowns as it utilizes your resources for unauthorized activities, such as sending out spam or communicating with command-and-control servers. To mitigate this risk, it is vital to conduct regular scans using reputable antivirus software. Upon detection of any malicious software, follow the recommended steps for removal to regain control of your network speed.
In addition to malware, background applications can significantly impact your internet speed. Many applications, such as cloud storage services, streaming platforms, and even system updates, may run in the background, consuming considerable bandwidth. To pinpoint these applications, open your device’s task manager or activity monitor. Here you can observe which applications are utilizing your internet connection. Once identified, consider closing or limiting the usage of these applications, especially during critical tasks that require faster internet speeds.
Configuration errors can also hinder your internet speed. These can arise from incorrect network settings or misconfigured software dependencies. Ensuring that your router settings are optimized and that your devices are properly configured for internet access is essential. Regularly check for software updates for both system software and interconnected devices. Keeping your software up-to-date ensures that you benefit from the latest stability enhancements and security patches, which ultimately aids in maintaining robust internet performance. By addressing these software issues, you can significantly improve your internet speed and overall connectivity experience.
Contacting Your Internet Service Provider
Experiencing persistent internet speeds that do not meet your expectations can be frustrating. When efforts to resolve issues independently have not yielded results, contacting your Internet Service Provider (ISP) becomes a necessary step. Before making a call, preparing certain information can greatly expedite the process and ensure effective communication.
First, gather all relevant account details, including your account number, the name associated with the account, and the service address. Additionally, make note of the date and time when the speed issues began, and document any troubleshooting steps you have already taken, such as rebooting the modem or testing speeds with different devices. This information will help the customer support representative assess your situation swiftly.
ISPs often have a set protocol for handling speed-related issues. Common troubleshooting steps you may encounter include checking for outages in your area, ensuring that your modem and router are functioning properly, and verifying that your equipment is compatible with the internet speed you are paying for. Your ISP may also suggest connecting your device directly to the modem to eliminate any potential issues caused by Wi-Fi interference. Be prepared for these standard recommendations as they help isolate the problem.
Consumers have rights regarding internet service, and it is essential to be aware of these as you navigate your ISP’s support system. If ongoing issues are not resolved satisfactorily, you may explore options such as requesting a bill adjustment or considering a service tier upgrade without additional costs. Understanding your rights empowers you in discussions with your ISP and can lead to a more favorable outcome. Ultimately, following this approach increases the likelihood of restoring internet performance quickly and efficiently.
Preventive Measures for Future Problems
Maintaining a stable and fast internet connection requires a proactive approach to avoid issues such as speed degradation. One of the fundamental preventive measures involves regularly conducting internet speed tests. By routinely measuring your connection speed, you can identify variations from your expected bandwidth, which may indicate underlying problems with your service or equipment. Various online tools are readily available to assist in this task, allowing you to track fluctuations over time.
Additionally, scheduled hardware checks are crucial in ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your internet setup. This includes inspecting your modem and router for any signs of wear or malfunction. Dust accumulation, loose cables, or outdated firmware can negatively impact performance. By routinely updating your equipment and ensuring that all components are in good working order, you can significantly reduce the chances of experiencing slow speeds.
Staying informed about new technologies is another effective strategy for maintaining a robust internet connection. The technology landscape evolves rapidly, with advancements that can enhance connectivity, such as Mesh Wi-Fi systems or new router standards. Upgrading to newer hardware when necessary can improve your overall experience, particularly if you find that your current equipment struggles to support your household’s demands.
Moreover, periodically evaluating your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is essential for optimal service. Customer satisfaction and service offerings can change, and what was once the best option may no longer suffice. Researching to compare plans, reviewing customer feedback, and checking for better service offers can help ensure that you are receiving the fastest internet speeds available to you.
Implementing these preventive measures can help maintain a consistently fast internet connection, thereby minimizing disruption to your online activities.